With technology’s constant evolution, the opportunities in the fintech world continue to expand. However, so do the risks – cybercrime has become more pervasive than ever, making a robust data governance framework essential for banks and fintech companies aiming to protect sensitive information and maintain customer trust.
Recent studies show that ransomware attacks have steadily intensified, with 65 percent of financial organizations worldwide reporting incidents in 2024, a significant increase from 55 percent in 2022 and 34 percent in 2021.
One of the biggest challenges organizations face today is meeting regulatory compliance standards – and for good reason. Strong data governance prevents financial crimes and guarantees client safety and trust. So, how do modern companies ensure compliance with data privacy regulations, and what role does AI play in this process?
Data governance best practices for financial institutions
The fintech market continues to expand rapidly, and according to Forbes, its size is expected to reach $698 billion by 2030. Given the influence and power of digital solutions, data has become one of the most valuable assets for any organization. With the growing adoption of fintech solutions, data management and governance have become essential pillars of success for any organization.
As the name suggests, data governance is the discipline responsible for ensuring data quality, security, and availability. Implementing the right data governance software and adhering to consistent best practices can empower banks and fintech companies to make more informed and safer, data-driven decisions. Strong customer data protection not only safeguards organizations from data leakage and financial crimes but also builds long-term trust with clients.
Among the most relevant data security and compliance standards are the following:
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR is a European privacy and security law that imposes obligations on any organization that collects or processes data related to individuals in the EU, regardless of where a service provider is based. Since May 2018, all businesses handling the data of EU citizens must adhere to strict data protection principles and accountability requirements. Non-compliance can result in costly fines, making it essential for fintech startups and financial institutions to carefully follow the regulations.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
The PCI DSS is a widely adopted set of policies and procedures designed to secure credit, debit, and cash card transactions. Industry experts developed it to protect cardholder data, including card numbers, expiration dates, and other sensitive information. Unlike the GDPR, PCI DSS is not a legal requirement, but rather a contractual obligation. This compliance represents best practices for fintech security, reducing the risk of fraud and data leakage incidents while ensuring data security and compliance across payment systems.
ISO/IEC 27001
The ISO/IEC 27001 is an international Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) standard that provides organizations with a structured framework for implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving cybersecurity measures. This structure allows organizations to anticipate evolving threats and create a culture of data management in financial services that supports business resilience and regulatory compliance. Banks and fintech companies can apply several data governance principles to improve consistency, minimize risk, and enhance performance. Some of the most effective best practices include:
Automate data-related tasks to increase efficiency.
Create a centralized data catalog.
Balance between data safety and convenience.
Continuously monitor, review, and improve data governance implementation strategies.
Common challenges in the data governance framework
Investors, customers, and regulators are increasingly demanding transparency and accountability from digital businesses – especially financial institutions that handle massive volumes of sensitive data. However, most firms struggle to implement effective data governance in the financial services sector. In 2023, approximately 93 percent of fintech companies reported difficulties in meeting data privacy compliance requirements.
Inconsistent data across systems
From large banks to smaller fintech startups, fragmented databases, legacy systems, and data silos are among the most common obstacles. These gaps lead to inconsistent or duplicate information, which can undermine business intelligence and make it nearly impossible to apply consistent data governance principles.
A solution to this challenge is for data architects to design appropriate data models and architectures that integrate information across different storage systems. Additionally, businesses may need to develop a comprehensive data catalog to manage their data assets effectively.
Constant demand for data
As financial services become more data-driven, businesses are under pressure to access and share information quickly without compromising security and compliance. While rapid insights are key to competitiveness, this constant demand increases exposure to data leakage protection risks and compliance failures.
To achieve balance, organizations must adopt clear data governance implementation strategies. Establishing strong encryption, access control, and continuous monitoring can help mitigate risks while maintaining efficiency.
AI data requirements
Artificial Intelligence adds another layer of complexity. One of the biggest drawbacks for digital companies is supplying quality data to train AI models while staying compliant with governance frameworks. This is especially true when it comes to data management in fintech, where handling sensitive information requires strict oversight and advanced security measures.
Unfortunately, many existing data governance tools still lack the adaptability needed to keep up with evolving AI ecosystems, leaving gaps that can expose organizations to regulatory and reputational risks. As fintech solutions continue to integrate AI, companies must strengthen their data governance best practices to safeguard both compliance and customer trust.
AI in data governance
The success and widespread adoption of artificial intelligence have amplified the demand for smarter and more efficient data governance frameworks. Across the financial services industry, fintech companies are increasingly relying on AI to enhance automation, risk prediction, and decision-making. However, the rapid application has also raised concerns among both investors and customers about data privacy compliance, ethical oversight, and the potential misuse of sensitive customer data.
At its core, AI depends on vast amounts of information to learn, recognize patterns, and generate accurate outputs. Regardless of how advanced large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT may appear, their effectiveness is rooted in one fundamental principle: the quality of an AI model is only as good as the data it’s trained on. This raises one of the most pressing concerns in data protection and fintech: balancing the responsible management of sensitive information with the need to ensure data security and privacy.
Many fintech solutions now integrate AI-powered data governance software to automate monitoring, classification, and compliance tasks. These tools enable organizations to enforce security and compliance measures in real time. However, the challenge intensifies when AI systems process highly sensitive data.

For example, if a customer decides to end their relationship with a company, GDPR requires the complete removal of their data from all systems. But if that information was used to train an AI model, the organization must retrain or decommission the model to comply – an expensive and complex process.
To mitigate these risks, organizations must integrate AI data governance best practices across the entire AI lifecycle. This includes implementing encryption, access controls, and clear audit trails, as well as ensuring transparency in how data is utilized and retained. Embracing artificial intelligence to support security strategies can be a game-changer.
In fact, according to IBM, organizations that applied AI and automation in their data governance implementations reduce the cost of data breaches and save an average of $2.22 million compared to companies that do not leverage these technologies.
The future of fintech security
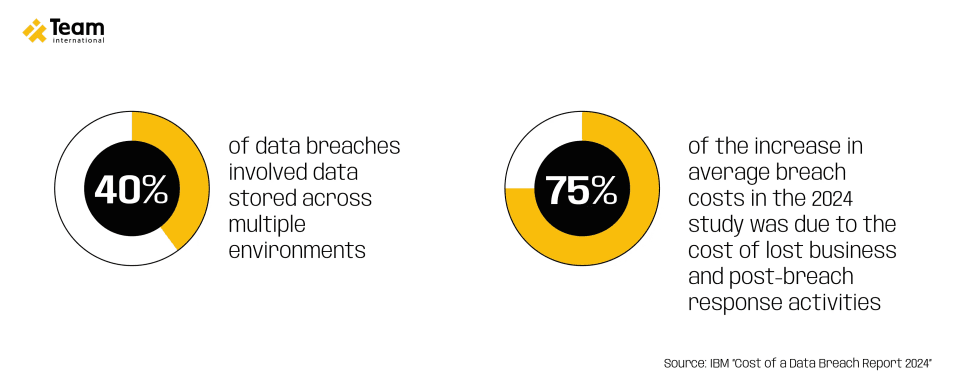
To stay ahead of the competition, you must anticipate regulatory trends and proactively strengthen your strategies, particularly in cybersecurity for fintech and the protection of sensitive data. And for a simple yet crucial reason, cyberattacks and data breaches are on the rise. In 2024, the average global cost of a data breach reached $4.88 million, with one in three breaches linked to shadow data.
Nowadays, AI can become one of the most essential tools for most industries. In fact, 84 percent of fintech companies now leverage AI and machine learning to meet compliance requirements. However, AI is not a set-it-and-forget-it solution – it demands strong oversight, effective leadership, and continuous monitoring to truly deliver value.
By implementing advanced cybersecurity measures, data privacy laws, and transparent communication, your company will ensure compliance and unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth, strengthening your investors' and customers' trust and loyalty to your business.
