Despite the growing momentum around AI in chemical manufacturing, the industry remains one of the least exposed sectors to its transformative potential. A recent McKinsey survey revealed that only 14 percent of activities in energy and materials are influenced by generative AI, compared to the 23 percent cross-industry average.
As global markets demand more sustainable production, agile supply chains, and faster innovation cycles, artificial intelligence offers a competitive edge beyond automation. Let’s explore how Gen AI reshapes production, its applications, and what executives need to consider to lead the digital transformation in the chemical industry.
The role of AI in chemical manufacturing
The chemical industry is one of the most essential sectors in the global economy. From agriculture to pharmaceuticals, it shapes the foundation of countless other industries. Yet, when it comes to adopting cutting-edge technology, it lags. According to McKinsey, while Amazon invested $73 billion in technology and infrastructure in 2022, the entire U.S. chemical industry spent just $13 billion. That gap speaks volumes about how chemical innovation has slowed, raising important questions about the future of chemical engineering.
Companies are turning to artificial intelligence to close that gap, but not all AI is created equal. Traditional AI excels at solving defined problems: it analyzes structured data, follows fixed rules, and automates known tasks like predictive maintenance or process optimization. Generative AI, on the other hand, opens new frontiers. It can process both structured and unstructured data and identify patterns humans might miss. It even supports AI-powered chemical processes that drive discovery and operational gains.
This growing interest in AI is part of a broader digital transformation already underway in the chemical sector. IBM’s report noted that companies invest in a wide range of technologies, from IoT and cloud computing to robotic process automation and AI. These advances accelerate automation in the chemical industry, but the real differentiator isn’t just the technology—it’s how effectively you implement it. To turn digital potential into measurable results, industry leaders must prioritize three essential pillars:
People and training: Empowering teams through upskilling is essential. Employees must understand the tools and the processes to boost digital transformation.
Data quality and architecture: Advanced systems require reliable, well-structured information to deliver accurate insights. Without a robust data infrastructure, optimization efforts stall.
Compliance and governance: As intelligent systems become embedded in regulated workflows, maintaining transparency, traceability, and regulatory alignment is non-negotiable.
AI applications in the chemical industry
The chemical industry has never lacked data—it thrives on it. But what companies need now is a smarter way to turn that data into decisions. Artificial intelligence offers exactly that: speeding up innovation, optimizing operations, and making better decisions at every value chain stage. From AI-enhanced chemical research to next-generation process control, intelligent technologies redefine what's possible in the lab and on the plant floor.
Let’s look at how it’s already reshaping the way the industry works:
1) Research and development
Finding a new molecule or material isn’t just complex—it’s slow and expensive. Traditional R&D cycles can stretch over several years and consume millions in funding before a single product reaches commercial scale. Generative AI accelerates that pace. From molecular discovery to formulation, it reduces what used to be months to weeks. Unlike conventional AI, which requires large datasets and predefined models, newer foundation models are far more data-efficient.
The result: Faster, more targeted innovation fueled by data-driven chemical manufacturing practices.
2) Process optimization and quality control
Chemical production processes are sensitive to small temperature, pressure, and input purity variations. AI-powered analytics can monitor these variables in real time, detect anomalies, and recommend or apply adjustments automatically. This leads to more stable production, fewer shutdowns, and improved product consistency, all while minimizing energy and resource consumption. In this context, AI in chemical production isn’t just about automation—it’s about unlocking new levels of efficiency and precision.
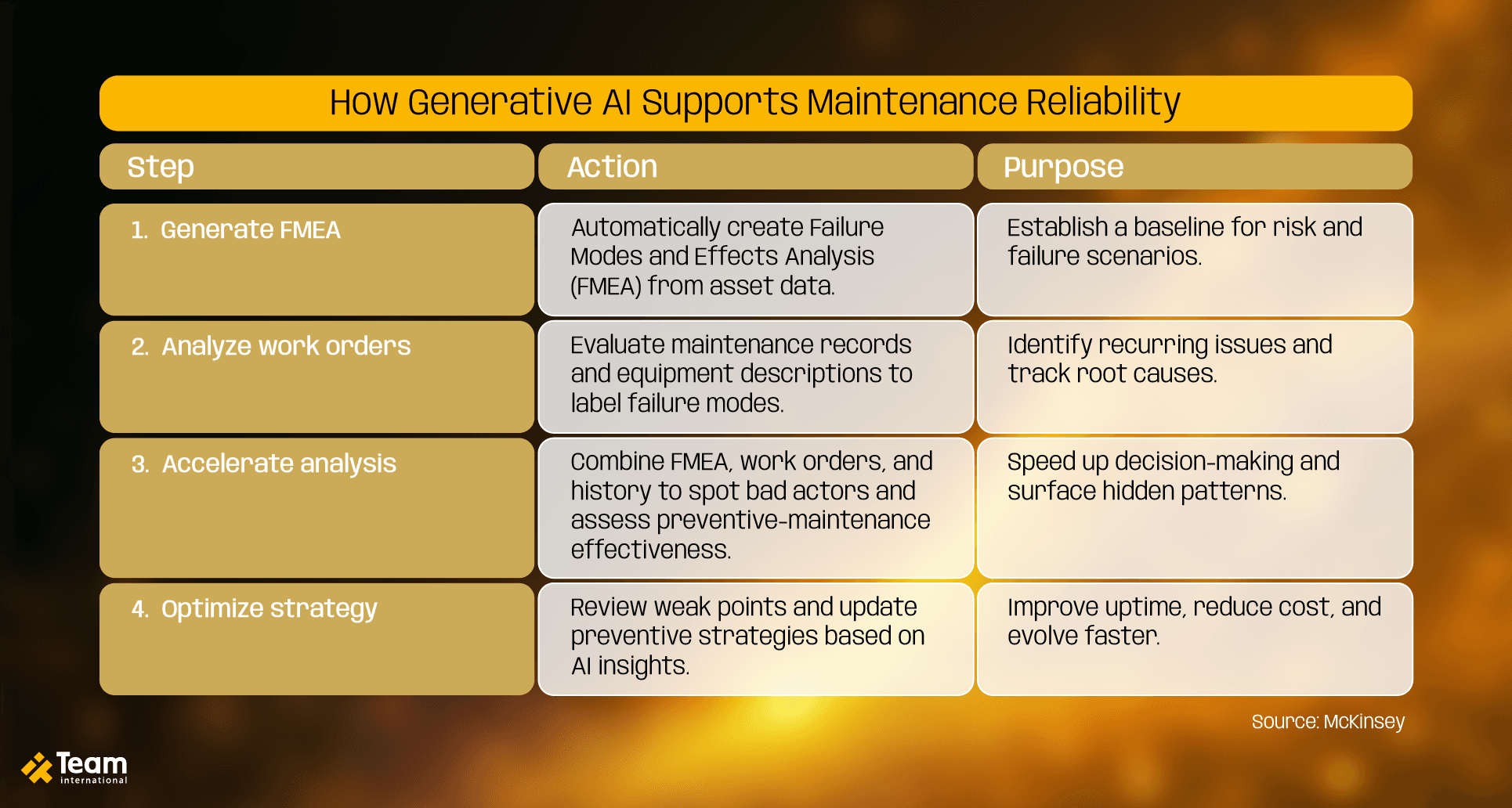
3) Predictive maintenance
Traditional maintenance approaches often rely on scheduled checks or historical failure patterns, but that’s no longer enough. With generative AI, companies are redefining how they approach reliability. By combining internal maintenance records with external data sources, they can automatically generate or refine failure modes and effects analyses (FMEA), helping their teams prioritize interventions based on actual risk and cost tradeoffs.
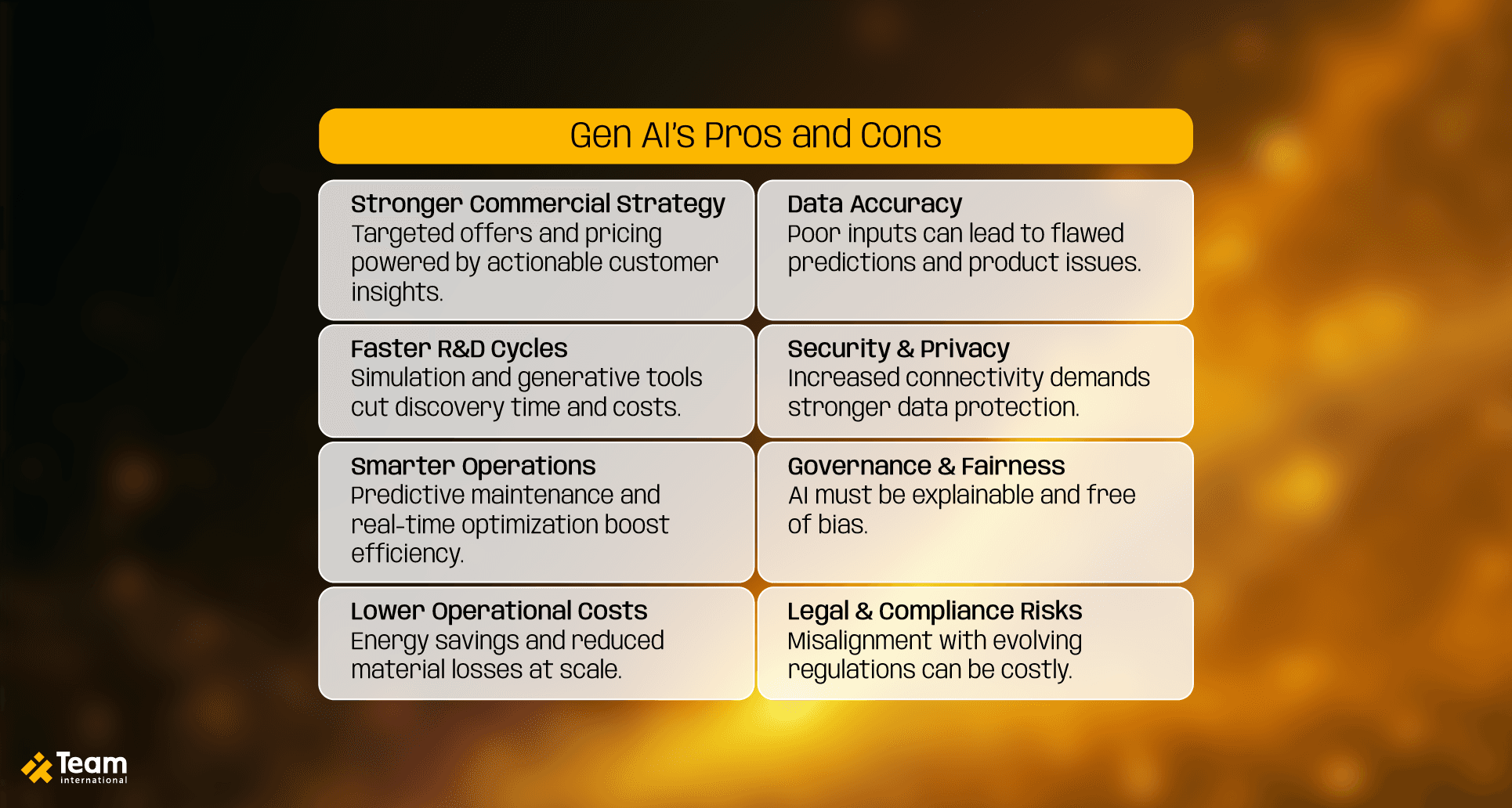
Benefits and challenges of Gen AI
AI-driven automation reshapes the entire chemical industry, from streamlining production lines to accelerating research and development. Whether through AI in chemical manufacturing or robotic process systems, the benefits are tangible: better performance, faster innovation, and smarter resource use. However, unlocking that value at scale comes with important considerations, especially for organizations operating in highly regulated environments.
Benefits
Commercial advantage: Intelligent automation tools help sales and marketing teams analyze customer behavior, tailor offers, and optimize pricing strategies. By unlocking deeper customer insights, your company can increase win rates, boost retention, and align offerings more closely with demand.
R&D acceleration: Automation dramatically reduces the time and cost of molecule discovery, testing, and formulation. With the help of AI in industrial chemistry, your teams can simulate outcomes, shorten iteration cycles, and bring innovations to market faster with fewer resources.
Operational efficiency: Predictive maintenance, process optimization, and real-time monitoring reduce unplanned downtime and increase throughput. These improvements highlight how automation in the chemical industry goes beyond routine tasks, enabling more intelligent decision-making and more agile production environments.
Cost optimization at scale: From reduced energy consumption to more innovative inventory planning and fewer material losses, automation strengthens the bottom line without sacrificing performance or compliance.
Risks
Accuracy: AI algorithms need clean, complete, and representative data to function correctly. In critical processes, flawed predictions can lead to product issues or safety risks.
Security and privacy concerns: Expanding connectivity increases exposure. Safeguarding sensitive production data, trade secrets, and customer information is now a strategic imperative.
Data governance and fairness: AI-driven decisions must be explainable and equitable. Avoiding biased outcomes requires robust oversight.
Legal and compliance risks: Evolving regulations around AI, digital data, and operational transparency add legal pressure. Missteps in these areas can lead to financial penalties or reputational damage.
The time is right for emerging leaders
From our experience supporting digital transformation across complex, highly regulated industries, one thing is clear: the time is right for intelligent automation in chemicals. If you're ready to move beyond pilots and scale artificial intelligence across your organization, success will depend on how well you align people, data, and AI governance. Do it with the right partner, and you won’t just boost performance—you’ll position your company at the forefront of innovation, agility, and market leadership.
